AI for Sysadmins and Developers (Part 2): A Guide to Self-Hosting LLMs with Ollama
Choosing the right AI model can be challenging. In this comparison, we break down open-source and proprietary models by cost, control, privacy, and performance, helping you make an informed and strategic decision for your specific needs.

Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Open-Source vs. Proprietary AI: Choosing between open-source AI (like Llama 3) and proprietary models (like GPT-4o) is a major strategic decision that balances control, cost, and privacy against cutting-edge performance and support.
- The Self-Hosting Challenge: While self-hosting an LLM offers maximum privacy and control, it comes with significant burdens, including high hardware costs, complex infrastructure management, and the responsibility of being your own support team.
- Practical AI for Daily Tasks: AI can be used today as a powerful co-pilot for generating scripts, creating configuration files, and debugging code, drastically improving productivity for sysadmins and developers.
- Getting Started is Easy: Tools like Ollama make it possible to run a powerful, private LLM on your own machine in minutes, providing a safe sandbox for learning and experimentation.
Table of Contents
- The Great Divide: Open-Source vs. Proprietary AI
- Making the Call: A Head-to-Head Comparison
- The Self-Hosting Decision: Freedom and its Burdens
- AI in Your Terminal: Putting it to Work Today
- Your First Self-Hosted LLM with Ollama
- Where Do We Go From Here?
Alright, welcome back. In Part 1, we got our hands dirty with the nuts and bolts of neural networks and mapped out the MLOps landscape. We talked gradient descent, the AI development lifecycle, and the hardware you need to make it all sing.
So, now what? It's time to move from theory to the terminal. This is where the rubber meets the road. We're going to tackle the big strategic calls you'll have to make. Do you bet on open-source, or pay for a proprietary model? What does it really take to host one of these things yourself? And most importantly, how can you start using AI to make your life easier, today?
Stick around, because we’ll cap it all off with a hands-on tutorial to get your first private Large Language Model (LLM) running on your own machine in minutes. Let's get to it.
The Great Divide: Open-Source vs. Proprietary AI
One of the first, and biggest, forks in the road you'll encounter is the choice between open-source and proprietary AI models. This isn't just a technical decision. It's a strategic one that impacts cost, control, security, and your freedom to innovate. For anyone in our world, this is the modern version of the age-old "build vs. buy" debate.
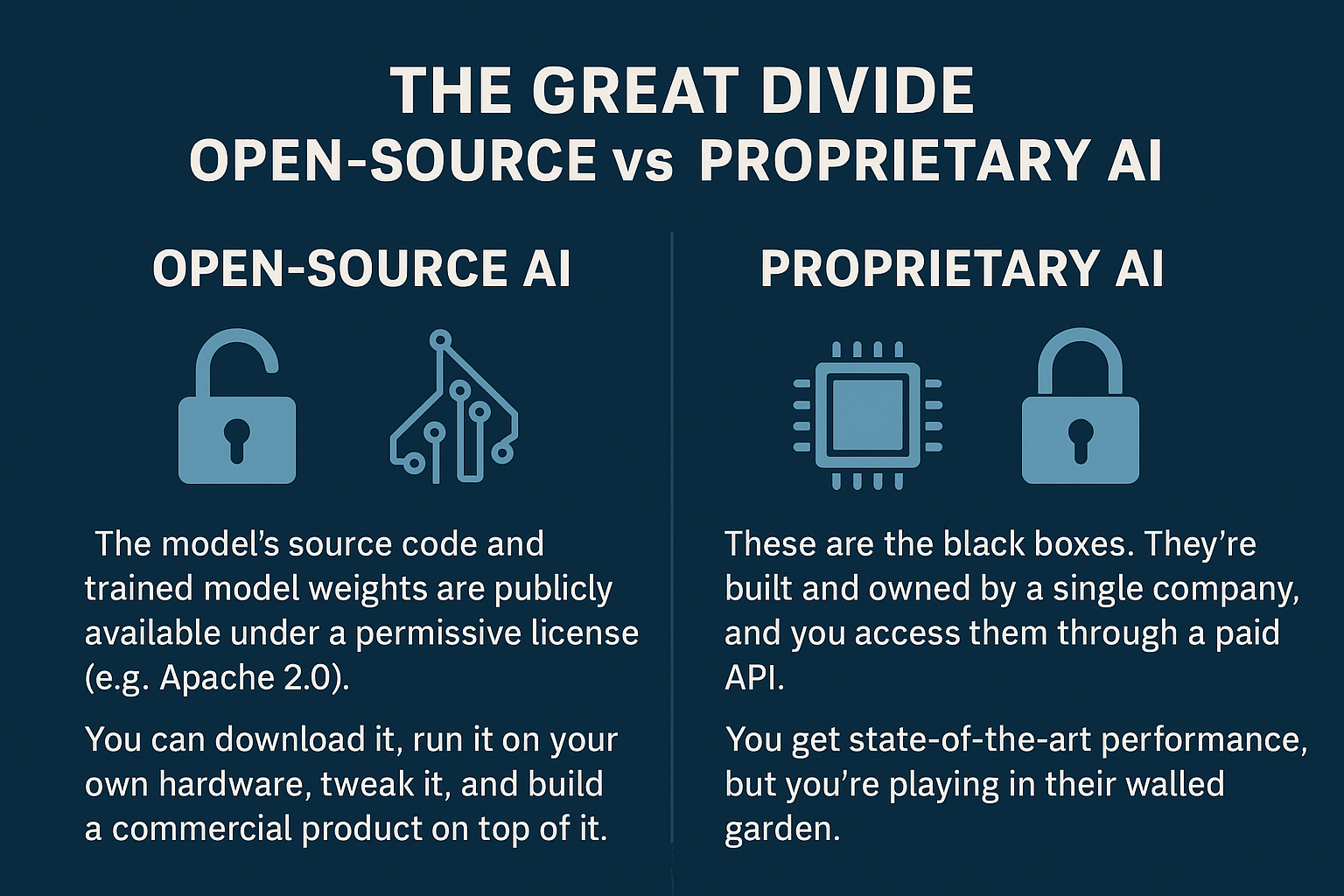
What "Open" Really Means
The term "open-source AI" gets thrown around a lot, but the landscape has shades of gray. It's crucial to know what you're actually getting.
- Proprietary (Closed-Source) AI: These are the black boxes. They're built and owned by a single company, and you access them through a paid API. You can't see the code, the model weights, or the data it was trained on. Think OpenAI's GPT-4o or Anthropic's Claude. You get state-of-the-art performance, but you're playing in their walled garden.
- Open-Source AI: Here, the model's source code and—this is the important part—the trained model weights are publicly available under a permissive license (like Apache 2.0). This means you can download it, run it on your own hardware, tweak it, and even build a commercial product on top of it. Meta's Llama family and models from Mistral AI are the big players here.
But be careful. "Open" isn't always truly open. Some models are released with strings attached, like non-commercial use clauses. Others might release the weights but keep the training data a secret, which makes it tough to know the model's biases. A truly open-source AI, as defined by the Open Source AI Definition (OSAID), gives you the freedom to use, study, modify, and share it for any reason.
Making the Call: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing your path means weighing a series of trade-offs. The "buy" option (proprietary API) gets you moving fast but locks you into a vendor. The "build" option (self-hosting open-source) is a heavier lift upfront but gives you ultimate control.
Let's break it down:
| Factor | Open-Source Models | Proprietary Models |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | No license fees. You pay for GPUs, power, and engineers. Often cheaper at scale. | No hardware costs. Pay per token or subscription — can become expensive quickly. |
| Control | Full control. You own the model weights, can fine-tune, and deploy anywhere. | Limited control. Bound by vendor API rules and infrastructure. |
| Privacy | Maximum — your data stays local. Ideal for sensitive or regulated industries. | Lower — data sent to a third party. Must trust vendor’s security and policies. |
| Performance | Rapidly improving. Open models now match last year’s top proprietary ones. | Still lead overall due to massive R&D and compute power. |
| Support | Community-based: GitHub, forums, Discord. No guaranteed SLA. | Enterprise-grade: official support, uptime guarantees, managed updates. |
| Vendor Lock-in | Low — portable across infrastructure and deployment stacks. | High — API-bound; switching providers is costly and complex. |
| Customization | High — modify architecture, train variants, or integrate with your stack. | Low — limited to fine-tuning or prompt templates. |
| Compliance | Full control to meet GDPR, HIPAA, or local regulations in-house. | Dependent on vendor’s compliance certifications. |
| Scalability | Scales with your own infrastructure. Needs optimization effort. | Instant scaling through APIs. Cost grows linearly with usage. |
Case Study: Llama 3 vs. GPT-4o
To make this real, let's compare two heavyweights: Meta's Llama 3 (open) and OpenAI's GPT-4o (proprietary). Llama 3 is the darling of the open-source world, known for its killer performance, especially in coding and reasoning. It's built for developers to grab and customize. GPT-4o is OpenAI's flagship, a beast of a model that's fast, incredibly intelligent, and handles text, images, and audio like it's nothing.
The key takeaway? The performance gap between open-source and proprietary is often a time gap, not a permanent quality gap. The best open models today are often as good as the best closed models from last year. (Data shows this time gap gradually narrows).
This opens up a powerful hybrid strategy I've seen work well. Start with a cutting-edge proprietary API to prototype and launch your feature quickly. At the same time, plan your migration to a self-hosted open-source model for when its performance is "good enough," letting you slash costs and take back control.
The Self-Hosting Decision: Freedom and its Burdens
For anyone who's ever run their own server, the pull of self-hosting is strong. Why self-host an LLM? Three huge reasons: total data privacy, predictable costs at scale, and the freedom to customize the model to your heart's content. And with tools like Ollama, you can get a powerful model running with a few commands.
But hold on. Running a model on your laptop is one thing. Running it in production is a completely different animal.
- The Hardware Bill is Real: You'll need enterprise-grade GPUs with substantial VRAM (think 24 GB and above), robust servers, and high-speed networking. This isn't just a server purchase; it's a significant capital investment. You're effectively building a small-scale AI data center.
- You Are the Support Team: When you self-host, everything is on you. Infrastructure, monitoring, security, patching, troubleshooting—it's all your problem. There's no vendor to call. When it breaks at 3 AM, you're the one grabbing the coffee and logging in.
- Performance is an Uphill Battle: Even with great hardware, you'll struggle to match the latency and throughput of the hyper-optimized infrastructure run by cloud giants. Squeezing every drop of performance out of a GPU is a deep engineering challenge.
Watch out for underestimating the sheer power and heat these GPUs kick out, forgetting to use Git for your configs, having no backup plan for your models, or creating a bottleneck by pairing a monster GPU with a weak CPU.
AI in Your Terminal: Putting it to Work Today
Enough about big decisions. Let's talk about the immediate payoff. AI isn't some far-off concept; it's a tool you can use right now to automate tasks and boost your productivity.
Your New Coding Partner
Think of AI not as a replacement, but as a force multiplier—a co-pilot for your daily grind.
Script & Code Generation: Need a PowerShell script to check for stale Active Directory accounts? Or a Bash one-liner to parse Nginx logs? Just ask. This is a massive timesaver. But (and this is critical) always treat AI-generated code as a first draft. These models can hallucinate commands, write insecure code, or just plain misunderstand you. You must review and test everything before it goes anywhere near production.
Configuration Files: You can also get a head start on configs for things like Docker or Kubernetes. But the quality of the output depends entirely on the quality of your input. Don't just say, "Give me a Dockerfile for a Node.js app." Get specific. Tell it to use multi-stage builds, a specific base image, and to handle caching. This is the essence of prompt engineering, which is quickly becoming a core technical skill.
Debugging and Explanation: This is where AI assistants truly shine. Paste in a cryptic chunk of legacy code, and it can explain it in plain English. Feed it a stack trace, and it can suggest a fix. It's like having an infinitely patient pair programmer on call 24/7.
AIOps: The End of Alert Fatigue
AIOps is about applying machine learning to the mountains of data our systems produce—logs, metrics, traces. The goal? To stop reacting to fires and start preventing them. Imagine this: instead of a single outage triggering 500 different alerts, an AIOps platform intelligently groups them into one incident tied to a probable root cause. It learns what "normal" looks like for your systems and flags anomalies before they cascade into failures. This is about reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) from hours of frantic log-diving to minutes of focused action.
Your First Self-Hosted LLM with Ollama
The best way to learn is by doing. Thanks to a fantastic tool called Ollama, running a powerful LLM on your own machine has gone from a weekend project to a five-minute task. Think of it like Docker, but for AI models.
Here’s how to get your Hello, World! for local AI up and running.
1. Install Ollama
On macOS or Linux, open a terminal and run:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
💡 Windows users can download the installer directly from Ollama’s website.
2. Download a Model
Next, pull a model. A great starting point is Llama 3 (8B) — an ideal balance between size and intelligence. Note: this download is about 4.5 GB and might take a few minutes.
ollama pull llama3
Windows users can choose which model to download directly from Ollama’s app.
3. Run and Chat!
You’re ready! Launch the model and start chatting — all locally, with zero data leaving your system.
ollama run llama3
Bonus: Add a Web UI
If you’d like a clean, ChatGPT-style interface, spin up Open WebUI with Docker:
docker run -d -p 3000:8080 --add-host=host.docker.internal:host-gateway \
-v open-webui:/app/backend/data --name open-webui --restart always \
ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
Then open your browser and visit http://localhost:3000.
Congratulations!!! You’ve just built a private sandbox for AI experimentation!
Running Open WebUI on Windows with Docker & WSL2
Where Do We Go From Here?
This wave of AI is a fundamental shift — much like the rise of cloud computing or DevOps. It’s not replacing us; it’s evolving what we do. Routine tasks will become automated, freeing you to focus on strategic and creative problems. Your role is transforming from system manager to architect of intelligent, autonomous systems.
The best part? Your existing expertise — Linux, networking, security, automation — is the perfect foundation for this new era. You’re not becoming obsolete; you’re becoming indispensable.
Your Roadmap
- Start Small: Use Ollama to explore. Automate one annoying task and learn by doing.
- Get Hands-On: Experiment with models, refine prompts, and build intuition through practice.
- Strengthen Your Core: AI runs on Linux, containers, and solid infrastructure — double down on your fundamentals.
What's Next?
In the following posts, we'll explore the power of automation tools like n8n and OpenAI Agent Builder.
We'll dive deep into OpenWebUI and how you can leverage it to build your own custom interface. This will allow you to chat with free, open-source models hosted directly on your device, as well as proprietary models from different providers—all in one convenient place.
Don't miss out on future posts and exclusive content—subscribe to my free newsletter today.
Ready to connect or explore more? Head over to my Linkedin profile